MEC多接入边缘计算及关键技术
1556 浏览 5 years, 8 months
6.1 Local Breakout 本地分流
版权声明: 转载请注明出处 http://www.codingsoho.com/移动数据的快速增长给4G网络以及未来的5G网络带来了极大的挑战,尤其是4G网络中数据面功能主要集中在核心网网关PGW上,并要求所有的数据必须经过PGW。然而此时,对于大量发生在网络边缘的业务流量(约35%),其长距离的迂回路由不仅增加了网络回传带宽的消耗及官网PGW的处理压力,更重要的是导致传输时间变长,业务体验变差。
大流量的视频数据迂回路由会导致几个问题:
- 回传带宽消耗过大
- 传输时延加大
- 业务体验不佳
本地分流/接入、选择性IP数据分流等需求很早受到了运营商的关注,借助LIPA (Local IP Access 本地IP接入)和SIPTO (Selected IP Traffic Offload 选择性IP数据流分流) 技术,实现通过家庭/企业基站(HeNB)进行数据分流、内部网络间的直接通信以及宏网络中特定IP数据流的直接分流,从而缓解核心网的传输负荷以及投资成本。
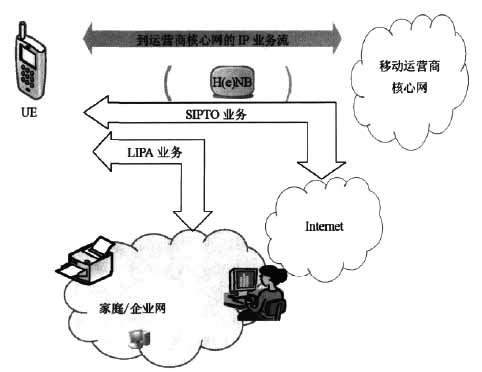
在LIPA场景中,终端用户通过H(e)NB,连接到同一个家庭/企业的IP网络中的其他网元上。此时,用户的数据流不会经过移动运营商的核心网,信令流依然会发送到移动运营商的核心网。
基于LIPA技术,终端用户与家庭网络中其他节点间的数据信息传递可以直接通过H(e)NB实现,而无需再传递到核心网节点,既能减少数据传输时延,也能减少核心网元的信令负荷降低核心网吞吐量和传输成本。
宏网络中的SIPTO技术可以把特定的IP地址的业务(例如对QoS要求不高的Internet业务)从终端接入的宏基站分流到一个特定的IP网络,以节省系统的传输资源。相比于现在所有的IP数据流都需要经过核心网,SIPTO允许在靠近用户的位置(如市、区等),分布式地部署网关设备(PGW),从而允许用户的数据能够从地理/逻辑更近的节点进行路由转发。可以看出,SIPTO既避免了IP流量迅速增加后对核心网压力的持续增加,另一方面,IP数据流就近路由转发可以提高路由转发效率,并可能因此避开核心网络资源的拥塞,提升用户的体验。
TR23.829
4.1.1 LIPA scenarios
According to TS 22.220 [3], LIPA breakout is performed in the same residential/enterprise IP network. Figure 4.1.1.1 illustrates this breakout at a Local GW (L-GW) in the residential/enterprise IP network.

Figure 4.1.1.1: LIPA breakout in the residential/enterprise IP network
4.1.2 SIPTO scenarios
According to TS 22.101 [2], SIPTO for Macro-Cellular breakout point is close to the UE's point of attachment to the access network, and that it shall be possible to support mobility for offloaded traffic, which means that the breakout point is "at or above RAN". Moreover, SIPTO for H(e)NodeB Subsystem allows the breakout to be located either in the residential/enterprise network as LIPA, or "above" H(e)NodeB in the hierarchical view of the mobile operator network i.e. in the backhaul or at the H(e)NodeB-GW.
As a consequence, two types of breakout architectures are distinguished:
- Architectures with breakout "at or above RAN" (covering macro and some H(e)NodeB SIPTO scenarios);
- Architectures with breakout "in the residential/enterprise IP network" (covering LIPA and some H(e)NodeB SIPTO scenarios).
In addition, selected IP traffic offload for the Home (e)NodeB Subsystem may support the following three scenarios:
- Scenario 1: Home (e)NodeB Subsystem and backhaul are provided by the same operator;
- Scenario 2: Home (e)NodeB Subsystem and backhaul are provided by different operators;
- Scenario 3: Local Breakout point (L-PGW) for LIPA/SIPTO is located in a private address domain, e.g. behind a NAT gateway.

Figure 4.1.2.1: A potential deployment case for scenario 3 where the local breakout point is behind a NAT gateway
5G MEC本地分流技术方案
参考文档
- 多接入边缘计算(MEC)及关键技术 - 第四章
- 3GPP. Local IP access and selected IP traffic offload (LIPA-SIPTO) (release 10): TR23.829[S].2011
- 3GPP. LIPA mobility and SIPTO at the local network (release 11): TR23.859[S].2011
- 3GPP System architecture for the 5G system TS23.501
- 3GPP Procedures for the 5G system TS23.502