MEC多接入边缘计算及关键技术
572 浏览 5 years, 8 months
5.3.3 Phase 3: client-side app and MEC app communication
版权声明: 转载请注明出处 http://www.codingsoho.com/A device application is logically separate from the actual client application (see Figure 6) which is the one requesting services from the MEC application. Any end user device may have the client application installed. A client application most often is unaware of the edge deployment of the server application, i.e. the MEC application. The device application, on the other hand, is needed for invoking user application lifecycle management operations on MEC system’s management plane, as explained in phase 3.
There are two ways for the client application to connect with a MEC application instance: The first option is that the developer/service provider takes responsibility for making the address of the MEC application, which it receives from the MEC system, available to potential client applications. The other option is that the client application discovers the MEC application instance via DNS look-up. If the domain name is owned by the application provider/developer, the developer needs to ensure that the domain name is managed and updated in the corresponding DNS server. The MEC platform supports the handling of MEC applications’ DNS records accordingly.
Depending on what functionalities are supported in the MEC system(s) where the application is being deployed the developer needs to support at least one of the two options above.
Figure 6 depicts the client-side application components; client application(s) and the device application, as well as the relevant MEC system components and the ways how the client-side application components can communicate with their MEC side peers. MEC platform been authorized to configure MEC application’s DNS records for a successful address resolution.
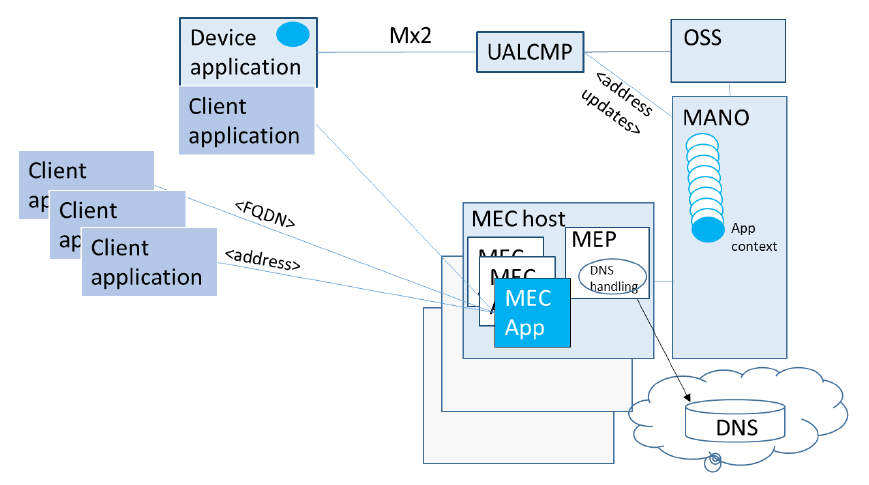
Figure 6: Communications between terminals and the MEC system